
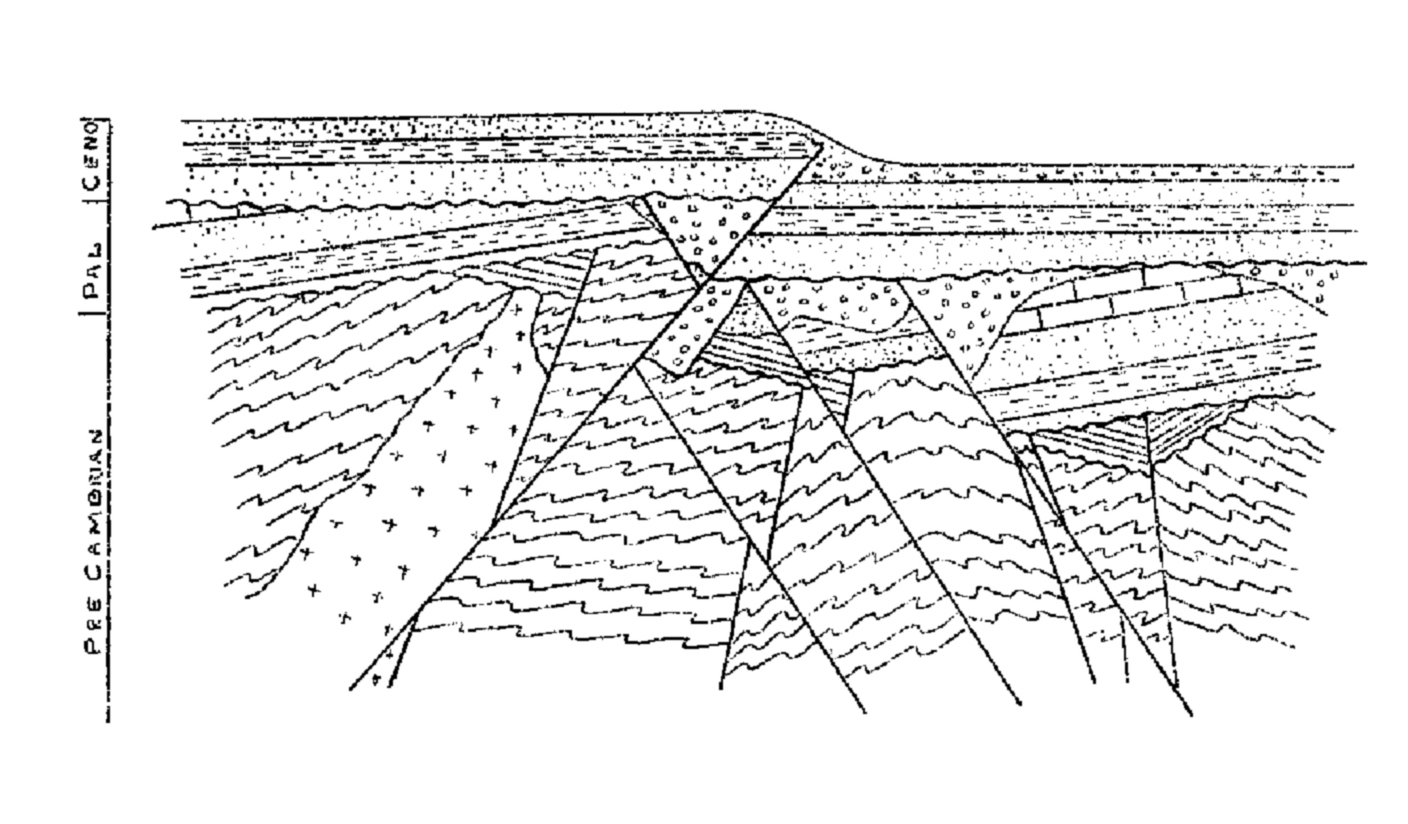
Labradorite, for example, is plagioclase with composition between 70% anorthite-30% albite and 50% anorthite-50% albite. Intermediate plagioclase compositions are commonly given specific names (labeled in the figure): oligoclase, andesine, labradorite, and bytownite.
We call any feldspar with composition near NaAlSi 3O 8, albite, and one with composition near CaAl 2Si 2O 8, anorthite, even if other components are present. Plagioclase, often called plagioclase feldspar, is mostly a solid solution of albite and anorthite, although it may contain up to 10 wt % orthoclase. Alkali feldspar, mainly solutions of orthoclase and albite, sometimes contains up to 15 wt % anorthite.
PHASE DIAGRAMS GEOLOGY SERIES
Natural feldspars form two distinct series, the alkali feldspar series and plagioclase, both labeled on this triangular diagram. In Figure 6.34, the blue region shows the compositions of naturally occurring feldspars. The important feldspar end members are albite (NaAlSi 3O 8), anorthite (CaAl 2Si 2O 8), and orthoclase (KAlSi 3O 8). For most purposes, we consider them to be ternary solutions, which means we can describe their composition in terms of three end members and plot them on diagrams such as the one shown in Figure 6.34 and in Figure 2.22 (Chapter 2). Rarely, they contain significant amounts of other elements such as Ba, Sr, B, or Fe. Feldspars are solid-solution minerals and have the general formula (Ca,Na,K)(Si,Al) 4O 8. They are widespread and are essential minerals in many igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. w l is the mass fraction of the whole sample in the liquid phase.\)įeldspars are the most abundant minerals in Earth’s crust, in part because they contain six of the seven most abundant elements in the crust. The same equations can be used to find the mass fraction of alloy in each of the phases, i.e. The tie line drawn is from the solid alpha to the liquid and by dropping a vertical line down at these points the mass fraction of each phase is directly read off the graph, that is the mass fraction in the x axis element. There is now more than one two-phase region.
PHASE DIAGRAMS GEOLOGY PLUS
Then the liquid concentration will start increasing.Įutectic phase diagrams Tie line in the Alpha plus Liquid two phase region If you're having difficulty realising why this is so, try visualising the composition when w o approaches w l. And then the denominator is the overall length of the arm so the difference between the solid and liquid compositions.
That is if you want the mass fraction of solid then take the difference between the liquid composition and the original composition. The numerator of each equation is the original composition that we are interested in is +/- the opposite lever arm. Where w B is the mass fraction of element B for the given composition (represented as w o in this diagram). In an alloy or a mixture with two phases, α and β, which themselves contain two elements, A and B, the lever rule states that the mass fraction of the α phase is It can be used to determine the fraction of liquid and solid phases for a given binary composition and temperature that is between the liquidus and solidus line. In chemistry, the lever rule is a formula used to determine the mole fraction ( x i) or the mass fraction ( w i) of each phase of a binary equilibrium phase diagram. Formula for determining the mole or mass fraction of phases in a binary phase diagram


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
